Practical Malware Analysis
Practical Malware Analysis - The Hands-On Guide to Dissecting Malicious Software by Michael Sikorski and Andrew Honig
Chapter 1 - Basic Static Techniques
- File signature: Identifiable pieces of known suspicious code.
- Heuristics: Behavioral and pattern-matching analysis.
- Hashing: Cryptographic fingerprint.
- Strings: Always end with a NULL byte.
- ASCII (1 byte per character).
- Unicode (2 bytes per character), always ends with a NULL byte.
- Packed programs:
- Compressed/obfuscated programs.
- Contains a wrapper/stub to unpack and run itself.
- Linked libraries:
- Static linking: Libraries are inside the executable.
- Runtime linking: Import libraries at execution (i.e. LoadLibrary, GetProcAddress...).
- Dynamic linking: The OS searches for the necessary libraries.
- Function naming conventions:
Exsuffix: Means a new version of the function (i.e. CreateFile & CreateFileEx).A(ASCII) orW(Wide) suffixes (i.e. FindFirstFileA & FindFirstFileW).
- Imported/Exported functions: List of imported and exported function by an executable or a library.
- PE file and sections:
- .text: Code instructions.
- .rdata: Import & export information, also read-only data used by the program.
- .data: Program's global data accessible from anywhere.
- .rsrc: Resources (icons, images, menus, strings...)
- Virtual & Raw Size: Virtual means in-memory and raw means on disk. If a section has no size on disk but a virtual size, this often means that it will be filled at runtime.
Chapter 2 - Malware Analysis in Virutal Machines
skipped...
Chapter 3 - Basic Dynamic Analysis
- Use a sandbox: Quick and dirty approach.
- Running a malware:
rundll32.exe name.dll,#1(or function name) - Monitoring:
- Process Monitor (ProcMon): You can filter on PID or Process name.
- Process Explorer Display: Process tree view (some processes could have been replaced by another, you need to compare memory).
- Regshot: Snapshot and comparaison of two registry.
- Network:
- ApateDNS or flare-fakenet-ng: Custom DNS to redirect and see network traffic.
- Wireshark: Open source sniffer.
- INetSim: Simulates commin Internet services.
Chapter 4 - Crash course in x86 disassembly
- C code => compiler => CPU Machine Code => Disassembler => Assembly Code
- Levels of Abstraction:
- Hardware: Electrical circuits that implements logical operations like XOR, AND, OR and NOT gates
- Microcode (firmware): An interface between hardware and machine code
- Machine code: List of Opcodes that tell the processor what to do
- Low-level languages: Human readable version of a computer architeture's instruction set (assembly).
- High-level languages: Programming languages like C, C++, ... Compiled to machine code.
- Interpreted languages: Programming languages like Python, C#, java, ... Translated to bytecode that will be executed by a interpreter.
- Microprocessors Architectures: x86, x64, SPARC, PowerPC, MIPS, ARM, etc.
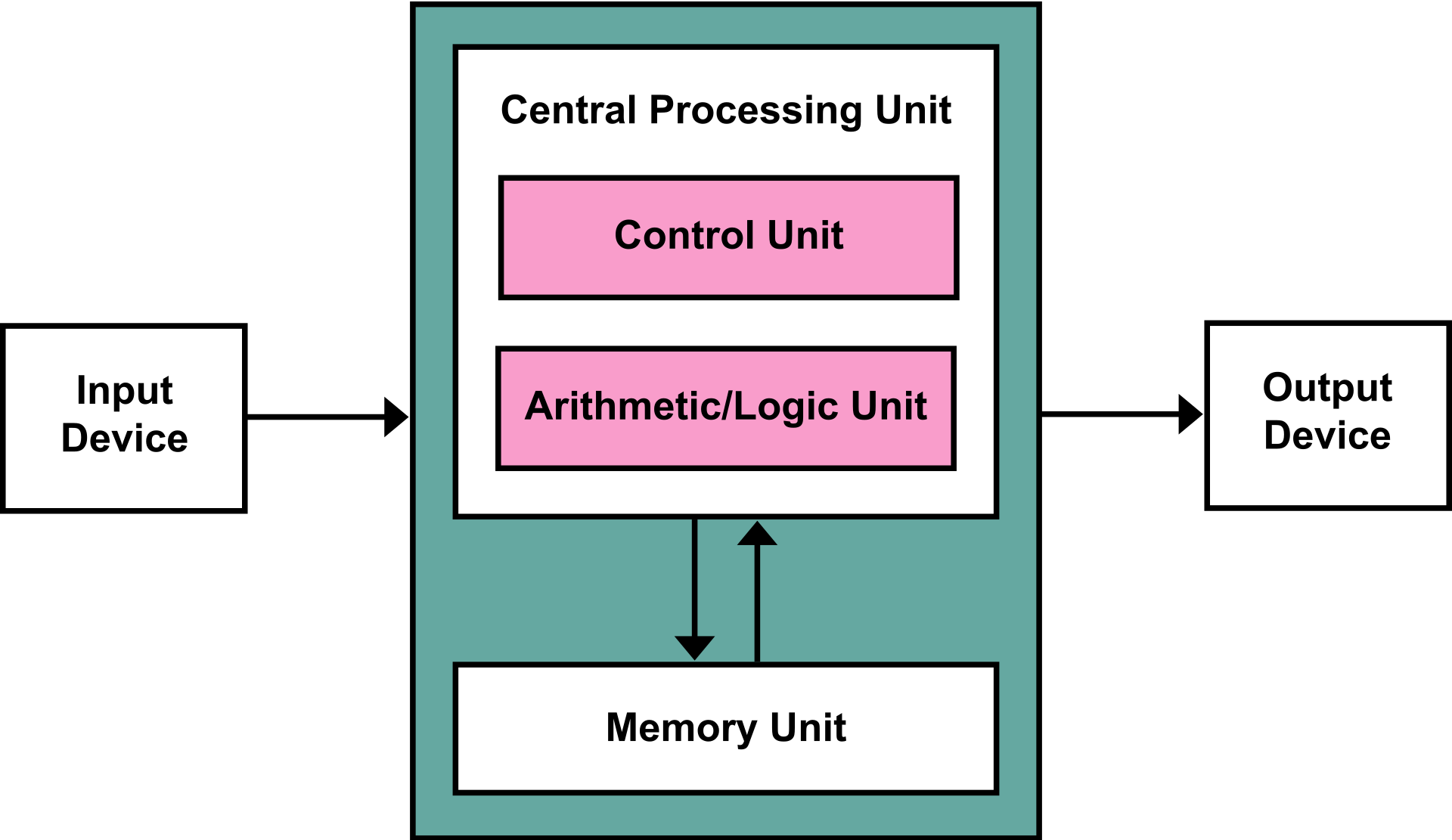
- Von Neumann Architecture:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Executes code
- Control Unit: Get instructions to execute from RAM using the Instruction Pointer register
- Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU): Executes an instruction fetched from the RAM and plces the results in memory/registers
- Main Memory: RAM
- Input/Output devices: Devices like keyboard, mouse, monitors...
- Opcodes and Endianness:
- Instructions:
mov ecx, 0x42 - Opcodes:
B9 42 00 00 00(little endian)
- Instructions:
- Registers:
- General registers: EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX, EBP, ESP, ESI
- Segment registers: CS, SS, DS, ES, FS, GS (track sections of memory)
- Status flags: EFLAGS (used to make decisions)
- Intruction pointer: EIP (address of the next instruction to execute)
- Flags:
- ZF (Zero Flag): Result is 0
- CF (Carry Flag): Result is too large/small
- SF (Sign Flag): Result is negative
- TF (Trap Flag): For debugging, execute one instruction at a time
- MOV vs LEA:
lea eax, [ebx+8]will put the address of EBX+8 into EAXmov eax, [ebx+8]will loads the data inside EBX+8 into EAX
- Multiplication and division:
| cmp dst, src | ZF | CF |
|---|---|---|
| dst = src | 1 | 0 |
| dst < src | 0 | 1 |
| dst > src | 0 | 0 |

- Rep Instructions: Set of instructutions for manipulating data buffers.
esi: source index,edi: destination index,ecx: counter- Rep instructions: Increments
esi&ediand decrementsecx - rep: Repeat until
ecx = 0 repe,repz: Repeat untilecx = 0orzf = 0repne,repnz: Repeat untilecx = 0orzf = 1- Operands of rep instructions:
Chapter 5 - IDA Pro
In a dedicated page on ctf-docs.
Tools
- Detect It Easy: Detect file and packed types.
- Dependencies: An open-source modern Dependency Walker.
- ProcMon: Process Monitor is an advanced monitoring tool for Windows.
- RegShot: Take a snapshot of your registry and compare it.
- FakeNet-NG: Dynamic network analysis tool.
- INetSim: Simulates common internet services.